2021.02
02.01
- Hadoop 클러스터 구축
- 인스턴스 4대
- Hadoop
- core-site.xml
- yarn-site.xml
- mapreduce.xml
- hdfs-site.xml
-
Spark 설치
- Spark와 Hadoop을 Yarn으로 엮고 있다.
- YARN 설정과 Spark 설정을 엮어야 되는데 잘 되지 않는다.
02.02
- Hadoop 클러스터 구축
-
YARN 설정
- Container 내 JAVA_HOME PATH 설정 오류
- Log 메세지
1
2
3
4
[2021-02-02 02:20:46.014]Container exited with a non-zero exit code 127. Error file: prelaunch.err.
Last 4096 bytes of prelaunch.err :
Last 4096 bytes of stderr :
/bin/bash: /bin/java: No such file or directory
- 해결방법
hadoop-env.sh파일 수정
1
2
3
# JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java -> 주석처리
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java
- Spark Job 테스트
Hadoop - Spark 연동을 확인하기 위해서 간단한 example spark job을 submit 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
spark-submit –class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
–master yarn \
–deploy-mode cluster \
–driver-memory 4g \
–executor-memory 2g \
–executor-cores 1 \
${SPARK_HOME}/examples/jars/spark-examples*.jar
spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--master yarn-client \
--num-executors 1 \
--driver-memory 512m \
--executor-memory 512m \
--executor-cores 1 \
${SPARK_HOME}/examples/jars/spark-examples*.jar 10
- SPARK java 경로 error
spark-env.sh에서 JAVA_HOME을 절대경로로 변경한다.
1
2
# spark-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64
- SPARK Session
1
org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RemoteException(java.io.IOException): File /user/hadoop/.sparkStaging/application_1612247239787_0001/__spark_libs__675299795277147897.zip could only be written to 0 of the 1 minReplication nodes. There are 3 datanode(s) running and 3 node(s) are excluded in this operation.
- hdfs namenode -format
- /tmp/hadoop-hadoop/data를 지움
1
sudo rm -R /tmp/*
- hdfs datanode -format
- 모든 데이터 노드 내 data 폴더 내 파일 제거(최후의 방법)
1
rm -rf /data/hd-cluster/data/*
- Dynamic Allocation 설정 에러
1
Exception in thread "main" org.apache.spark.SparkException: Dynamic allocation of executors requires the external shuffle service. You may enable this through spark.shuffle.service.enable
spark-defaults.conf
1
spark.shuffle.service.enable true
- Zeppelin 설치
- PySpark를 할 때에 Worker에 python 설정이 되어 있어야 한다.
- python 설정
1
2
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3 1
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/pip pip /usr/bin/pip3 1
TODO
- Ambari 설치
- Hue 설치
- [Future] 사내 Nas, Amazon S3 HDFS 연결
02.03
- Elastic Search - Hadoop - Spark 연동 구성 정리
- Hadoop Cluster Monitoring
- Ambari 외 다른 대안을 찾아야할 듯
- Server Performance Key indicator
- Disk
- Network
-
file
- references
https://www.eginnovations.com/blog/server-performance-monitoring/ https://www.monitis.com/blog/essential-server-performance-metrics-you-should-know-but-were-reluctant-to-ask/ https://raygun.com/blog/server-performance-metrics/
02.04
- Server Performance Monitoring 지표
- PySpark 연결 완료
- Elastic Search 인덱스 설계 방향
- Metric Beats에서 수집하고 있는 데이터에 대한 분석이 필요함.
- 참고 자료 CPU 프로파일링 /proc/stat python 프로그램 Disk I/O 모니터링을 위한 iostat 명령어 활용법 리눅스 I/O 트러블 슈팅(I/O Trouble Shooting)
02.05
Memory
HugePage
컴퓨팅에서 가상 메모리는 메모리 관리 기술이다. 스토리지 자원을 활용해서 가상의 큰 메모리를 사용하는 것처럼 바꾼다. OS에서는 프로그램에서 사용해야하는 가상 주소(Virtual Address)를 실제 물리 주소(Physical address)와 맵핑하는 작업을 대신 해준다.
Paging
메모리 관리 기술 중에 하나이다. 운영체제는 페이지라는 동일크기의 블록을 보조 저장소에서 데이터를 페이징은 프로그램이 사용 가능한 실제 메모리의 크기를 초과하도록 보조 저장소를 사용한다.
프로세스는 자신만의 가상 주소 공간을 가지고 있다. 32bit/64bit -> 최대 4GB/16EB의 주소 공간을 가진다.
특정 프로세스 내에서 쓰레드가 수행될 때 해당 쓰레드는 프로세스가 소유하고 있는 메모리에 대해서만 접근 가능 A 프로세세스가 0x12345678 주소에 무언가를 저장하였지만 B 프로세스도 0x12345678에 저장 될 수 있ㅇ음
Logical memory > Physical Memory를 가능하게 하는 것이 Virtual Address, Viru
- Demanding-Paging 기법
디스크 공간을 메모리처럼 활용할 수 있음 디스크 상에 존재하는 이러한 파일을 Paging file (swap file)이라고 하며 모든 프로세세스가 사용할 수 있는 가상 메모리로 사용 된다.
- Hard swap
페이징 파일에서 실제 물리 메모리로 올리고 내리리고 하는 일련의
- Page
가상메모리를 사용하는 최소 크기 단위 윈도우 운영체제 4096(4KB)의 페이지 크기를 사용한다.
페이징 파일에서 물리 메모리로 데이터를 로드 할 때, 아무 위치에 각자가 필요한 용량 만큼 올린다면 메모리 공간에 아무도 쓸 수 없는 짜투리 공간이 발생하게 된다. 이를 막기 위해서 Page라는 최소 크기 단위를 만듬
- Demanding Page 실제로 필요한 Page만 물리메모리로 가져오는 방식 필요 Page에 접근하기 위해서 가상 메모리 주소에 대응하는 물리 메모리 주소를 찾아내야함.
Linux Kernel 5 - Virtual Memory & Paging
02.08
CPU Metric 항목 분석
항목
- idle
- iowait
- irq
- nice
- softirq
- steal
- system
- total
- user
참조
- CPU Steal Time의 원인과 대책
- https://brunch.co.kr/@leedongins/75
- Metric beats CPU source code
- Accurate calculation of CPU usage given in percentage in Linux?
- Metric beats CPU source code
- Sigar github repository What does ‘nice’ mean on CPU utilization graphs?
- ticks 의미 찾기
- User section 조사하기
02.09
- system.user 항목 분석
- metric beats 정의
- logged in users and associtated session via dbus and logind, which is systemd component.
/var/run/dbus를 살핀다
dbus
Desktop Bus는 같은 머신에서 동시에 실행 중인 여러 컴퓨터 프로그램(프로세스) 간의 통신을 가능케 하는 소프트웨어 버스. 프로세스간 통신, 원격 프로시저 호출 매커니즘이다.
예시
- 오피스 제품군은 워드 프로세서와 스프레드 시트간의 데이터 공유를 위한 세선 버스를 통해 통신할 수 있다.
- Fields
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39
{ "@timestamp": "2017-10-12T08:05:34.853Z", "event": { "dataset": "system.users", "duration": 115000, "module": "system" }, "metricset": { "name": "users", "period": 10000 }, "process": { "pid": 10786 }, "service": { "type": "system" }, "source": { "ip": "192.168.1.86" }, "system": { "users": { "id": 6, "leader": 10786, "path": "/org/freedesktop/login1/session/_36", "remote": true, "remote_host": "192.168.1.86", "scope": "session-6.scope", "seat": "", "service": "sshd", "state": "active", "type": "tty" } }, "user": { "id": "1000", "name": "alexk" } }
| 메트릭 | 설명 | 사용 필요 |
|---|---|---|
| id | The ID of the session | |
| leader | The root PID of the session | |
| path | The DBus object path of the session | |
| remot | A bool indicating a remote session | |
| remote_host | A remote host address for the session | |
| scope | The associated systemd scope | |
| seat | An associated logind seat | |
| service | A session associated with the service | |
| state | The current state of the session | |
| type | The type of the user session |
Linux 명령어 loginctl 로 파악함
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
root@hadoop-cluster-1:~# loginctl list-sessions
SESSION UID USER SEAT TTY
1210 0 root
312 0 root
233 0 root
307 1002 hadoop
1 0 root seat0 tty1
305 1002 hadoop
220 0 root
1211 0 root
8 sessions listed.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
root@hadoop-cluster-1:~# loginctl show-session 1210
Id=1210
User=0
Name=root
Timestamp=Tue 2021-02-09 05:39:02 UTC
TimestampMonotonic=1112986312830
VTNr=0
Remote=yes
RemoteHost=36.243.190.1
Service=sshd
Scope=session-1210.scope
Leader=2225
Audit=1210
Type=tty
Class=user
Active=yes
State=active
IdleHint=no
IdleSinceHint=0
IdleSinceHintMonotonic=0
LockedHint=no
–> 딱히 성능적인 부분과는 크게 영향이 없을 것으로 판단됨.
02.16
- Memery Metric 분석
- Network metric 분석
- Process Metric 분석
02.17
- DiskIO Metric 분석
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
{
"@timestamp": "2017-10-12T08:05:34.853Z",
"event": {
"dataset": "system.diskio",
"duration": 115000,
"module": "system"
},
"metricset": {
"name": "diskio",
"period": 10000
},
"service": {
"type": "system"
},
"system": {
"diskio": {
"io": {
"time": 1296
},
"iostat": {
"await": 0,
"busy": 0,
"queue": {
"avg_size": 0
},
"read": {
"await": 0,
"per_sec": {
"bytes": 0
},
"request": {
"merges_per_sec": 0,
"per_sec": 0
}
},
"request": {
"avg_size": 0
},
"service_time": 0,
"write": {
"await": 0,
"per_sec": {
"bytes": 0
},
"request": {
"merges_per_sec": 0,
"per_sec": 0
}
}
},
"name": "sda6",
"read": {
"bytes": 335872,
"count": 82,
"time": 1296
},
"write": {
"bytes": 0,
"count": 0,
"time": 0
}
}
}
}
Disk Performance Concept
Measuring Time
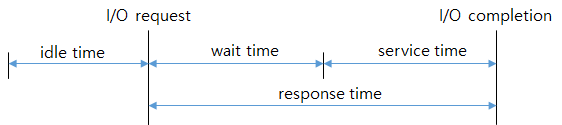

tps
- 디스크 장치에서 초당 처리한 입출력의 작업 갯수
- name
- io.time
- total number of time spent
- iostat.await
- 평균 시간 request가 디스크에 issued 될 때까지 특정 디바이스에
- iostat.queue.avg_size
-
iostat.read.await
- iostat.read.per_sec.bytes
- total
- iostat.read.request.merges_per_sec
-
iostat.read.request.per_sec
- iostat.request.avg_size
-
iostat.service_time
- iostat.write.await
- iostat.write.per_sec.bytes
- iostat.write.request.merges_per_sec
-
iostat.write.request.per_sec
- read.bytes
- 디스크 장치에서 초당
- read.count
-
read.time
- write.bytes
- write.count
- write.time
20초 DID
현실적 DiskIO로 인한 병목 현상 발생시 해결방안
- Application Level에서의 불필요한 Disk I/O 발생하는 지 점검(Log level 등)
- OS에서 제공하는 파라미터 튜닝을 통한 개선(Disk Queueing Algorithm 변경)
- linux에서 Noop, Deadline, Anitcipactory, CFQ등 write로 인한 read 지연을 개선 할 수 있음
- Disk 분산을 통한 I/O Bandwidth 개선
- I/O가 편준되는 FileSystem에 대해서 Volume을 물리적으로 여러 Disk로 분산하여 재구성한다.
참조
02.18
- Load 메트릭 분석
- Filesystem 메트릭 분석
filesystem
여러 개의 물리적 Disk를 가지며 각 Disk는 하나 이상의 filesystem을 갖는다. Kernel은 논리적 수준에서는 DIsk가 아니라 Filesystem을 다루며 file system 논리적 Device를 다룬다.
File - 어떤 정보의 모임, 보통 보조기억장치(디스크)에 저장됨 Filesystem - File들의 집합이 적절한 형태로 구성되어 있는 것
Filesystem이 나온 이융 저장 장치에 파일을 썼다 지웠다하게 되면 Fragmentaion이 발생하게 된다. 새로운 파일이 생성될 때 디스크의 빈 공간을 찾아서 쓰게 되는데 나중에는 하나의 파일이 연속적인 디스크 공간에 있지 않게 된다. 그렇게 되면 Disk seek time이 더욱 많이 발생하게 된다. -> 새로운 알고리즘 등장
Unix에서 있어서 File은 모든 바이트들이 논리적으로 한줄로 연결된 것 처럼 인식하게 한다.
02.19
- fsstat
system.fsstat.count
system.fsstat.total_files
system.fsstat.total_size.free
system.fsstat.total_size.used
system.fsstat.total_size.total
섹션 수집항목 실제데이터 계산값 fsstat system.fsstat.count 89 fsstat system.fsstat.total_files 59544532 fsstat system.fsstat.total_size.free 246,309,601,280 fsstat system.fsstat.total_size.used 631,553,163,264 fsstat system.fsstat.total_size.total 877,862,764,544 total = free + used 877,862,764,544
fsstat은 호스트가 가지고 있는 디스크와 연결된 모든 파일 시스템에 대한 통계를 보여준다. 각 디스크에 대해서 구할 수가 있으며 filesystem 자체는 성능에 대한 이슈와 상관 없을 것을 보인다.
확인해보아야할 것
- filesystem 섹션을 통해서 각각의 시스템을 구할 수 있고 이를 통해서 통계적인 것도 확인할 수 있다.
-
이것이 모두 통합된 것이 필요할 것인가? 아니면 es에서 sum을 하는 게 나을 것인가ㅐ
- uptime
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
{
"system" : {
"uptime" : {
"duration" : {
"ms" : 7506965000
}
}
}
}
- process
- process.summary
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
{
"system" : {
"process" : {
"summary" : {
"zombie" : 0,
"running" : 0,
"stopped" : 0,
"sleeping" : 753,
"unknown" : 0,
"idle" : 183,
"dead" : 0,
"total" : 936
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
GET sym-metric-process_summary-2021-02-19/_search
{
"size": 20,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "terms": {
"metricset.name": ["process_summary"]}},
{ "match": {
"host.hostname": "dev-controller"
}
}
]
}
}
}
02.22
- Core Metric 분석
- Locust를 활용한 부하 테스트
- 테스트용 어플리케이션
02.23
- Locust Sample 코드 작성
- Elastic Search - Spark 연동
02.24
- Hadoop zeppelin에서 pyspark, ES와 연동
- 실제 Metric 데이터 확인
- Python Directory 구조 생성
- Jupyter notebook을 이용한 Spark job 개발 환경 구축k
02.26
- PySpark Template Code 작성
- 공통 모듈 작성
- 부하 테스트 실행하기
Sample Test
- MariaDB 외부 설정
/etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.conf에서 bind-address 주석 처리root계정 0.0.0.0으로 열기GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'root';FLUSH PRIVILEGES;